Why Consider a Vegan Diet?
Imagine going to your favorite restaurant and ordering a meal that’s entirely plant-based—no meat, no dairy, but still delicious and filling. For many, the idea of a vegan diet can seem overwhelming or restrictive. However, more people are turning to veganism not only for health reasons but also for ethical and environmental concerns.
A vegan diet offers numerous health benefits, including reduced risks of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It also contributes to environmental sustainability by lowering the carbon footprint and conserving natural resources. In this post, we’ll dive into the essential aspects of veganism, including its health benefits, common misconceptions, and practical tips for transitioning.
What is a Vegan Diet?
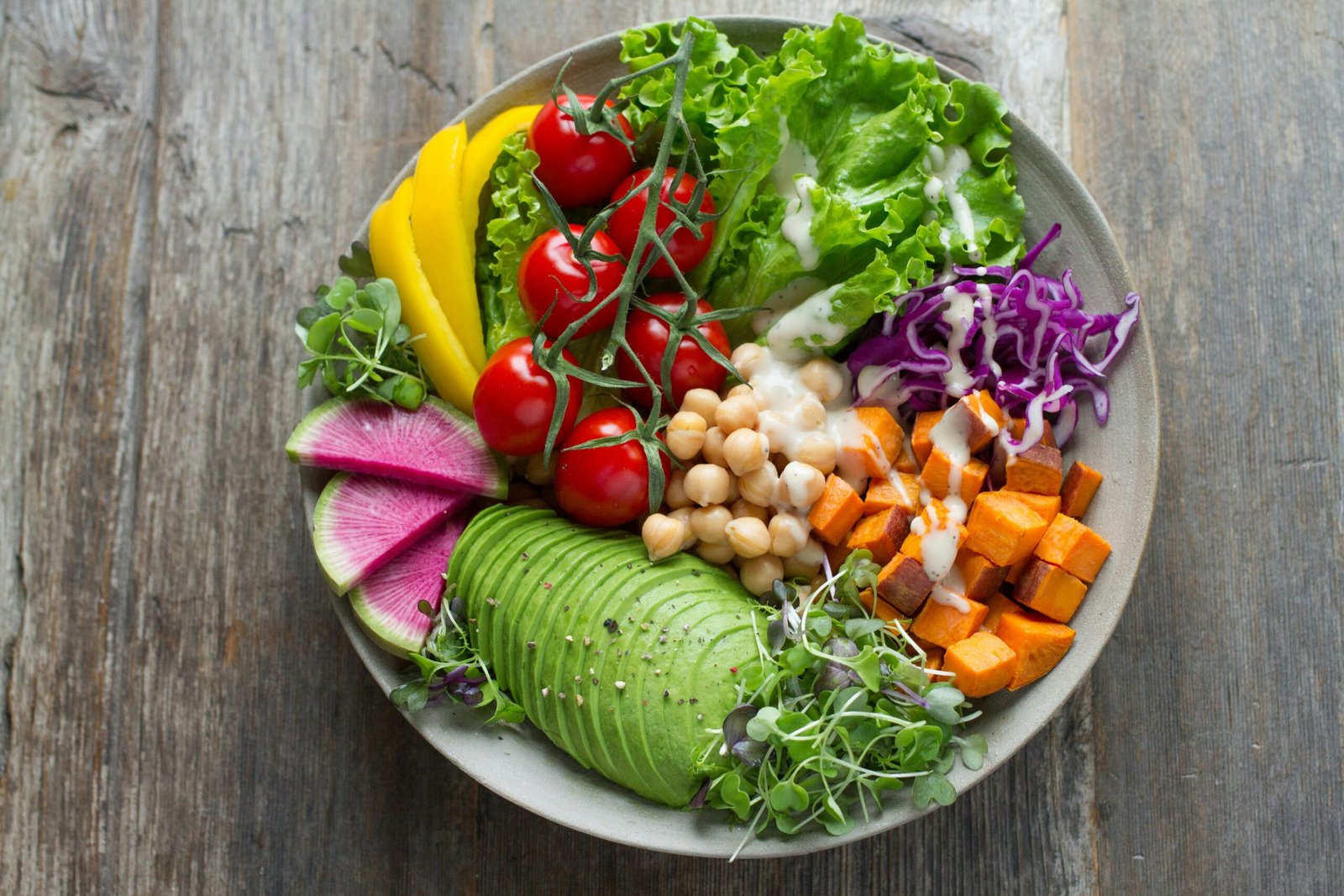
A vegan diet is one that excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and sometimes honey. This plant-based diet focuses on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Beyond dietary changes, veganism often aligns with a lifestyle choice aimed at reducing harm to animals, conserving resources, and promoting sustainability.
According to Wikipedia, veganism is a lifestyle that seeks to avoid the exploitation of animals for food, clothing, or any other purpose. The popularity of vegan diets has surged in recent years due to growing awareness of animal rights, climate change, and health.

Health Benefits of a Vegan Diet
Adopting a vegan diet can significantly improve your overall health. Several scientific studies have highlighted the benefits of plant-based eating:
1. Improved Heart Health
Studies have shown that vegan diets are linked to a lower risk of heart disease. The American Heart Association states that plant-based diets, which are naturally lower in saturated fats and cholesterol, promote healthier blood pressure and cholesterol levels. By focusing on plant-based foods, vegans can reduce their intake of harmful fats, leading to better cardiovascular health.
2. Weight Loss and Weight Management
Many people choose a vegan diet to support weight loss. Since plant-based foods are typically lower in calories and high in fiber, they help keep you full longer and reduce the risk of overeating. According to the WebMD overview, vegans tend to have lower body mass indexes (BMIs) compared to non-vegans.
3. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
A vegan diet is rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that are essential for disease prevention. By reducing processed foods and increasing whole plant-based foods, vegans experience a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and obesity. Research from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health suggests that plant-based diets lower the risk of chronic diseases due to the higher intake of plant-derived nutrients.
4. Better Digestion
A vegan diet is high in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain healthy bowel movements. Fiber-rich foods like beans, lentils, and vegetables promote gut health, helping to reduce the risk of digestive issues such as constipation.
How to Get Enough Protein on a Vegan Diet
A common concern for many people new to veganism is protein. However, there are plenty of plant-based protein sources that meet nutritional needs:
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are rich in protein and fiber.
- Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based products are excellent protein alternatives to meat.
- Seitan: A high-protein wheat-based meat substitute.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds provide healthy fats and protein.
- Quinoa: A complete protein source containing all essential amino acids.
According to scientific research cited in the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, a vegan diet can meet all protein needs if properly planned. With a balanced approach, vegans can maintain muscle mass and support body functions effectively.

Nutritional Requirements for a Vegan Diet
While a vegan diet offers many health benefits, certain nutrients need special attention:
1. Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation. Since it is found almost exclusively in animal products, vegans must consume fortified foods (such as plant milks, cereals, and nutritional yeast) or take a B12 supplement to avoid deficiency.
2. Iron
Iron in plant-based foods is non-heme iron, which isn’t as easily absorbed by the body as the heme iron found in meat. Vegans should include iron-rich foods such as lentils, tofu, spinach, and fortified cereals. Pairing these foods with vitamin C—found in citrus fruits, tomatoes, and bell peppers—helps enhance iron absorption.
3. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s are important for heart and brain health. Vegans can get omega-3s from flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algal oil supplements, a plant-based source of DHA.
Vegan Meal Planning for Beginners
Meal planning is crucial for a balanced vegan diet. Here’s how to get started:
1. Start Slowly
Don’t rush the transition. Begin by replacing one meal a day with a plant-based option. For instance, swap your regular lunch for a vegan salad or a chickpea wrap.
2. Include a Variety of Foods
Ensure you get a variety of nutrients by including a range of foods. Focus on whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and healthy fats like avocados and nuts. Include fortified foods like plant milks and cereals to meet your B12 and calcium needs.
3. Batch Cooking
Prepare meals in bulk, such as soups, stews, and curries, that you can store for several days. This makes it easier to stick to your plant-based diet.

Common Misconceptions About Vegan Diets
Despite its many benefits, there are some myths about veganism that need addressing:
1. “Vegans Don’t Get Enough Protein”
This is a common misconception. As discussed earlier, there are plenty of plant-based protein sources that provide the necessary nutrients to maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
2. “Vegan Diets Are Expensive”
While specialty vegan products can be costly, a whole food plant-based diet doesn’t have to break the bank. Staples like beans, rice, and seasonal vegetables are affordable and nutritious.
3. “A Vegan Diet is Hard to Follow”
With the increasing availability of vegan-friendly products and recipes, maintaining a vegan diet has never been easier. Grocery stores now offer a wide range of vegan alternatives, and countless online resources provide vegan recipes and meal plans.
Transitioning to a Vegan Diet
Transitioning to a vegan diet doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are some tips to make the process smoother:
- Start Gradually: Begin by eliminating one animal product at a time. Start with dairy, or try Meatless Mondays to ease the transition.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about vegan nutrition and cooking. The more you know, the easier it will be to make the right choices.
- Find Support: Join vegan communities or consult a nutritionist for personalized guidance.
Environmental and Ethical Reasons for Choosing a Vegan Diet
Many people turn to veganism for ethical reasons, including animal welfare concerns and the desire to reduce their environmental footprint. By eliminating animal products, you reduce the demand for factory farming, which is a leading cause of deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water waste. According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), adopting a plant-based diet can help mitigate climate change and preserve natural resources.
Is a Vegan Diet Right for You?
The vegan diet offers numerous health benefits and a way to live more ethically and sustainably. Whether you’re motivated by health, the environment, or animal welfare, veganism provides a path to better living. By carefully planning your meals and ensuring adequate nutrient intake, you can thrive on a vegan diet. Transitioning to veganism may take time, but with the right support and resources, it can be a rewarding journey.